
Teamwork, cooperation, creativity and adaptation to change, to name a few aspects of Arts. The prevalence of automation has created a growing demand for workers with social skills. Having a strong set of soft skills helps employees become more versatile and can open up more opportunities for growth in today’s job market.
This demand for soft skills has led to the creation of new curricula to help prepare those aspiring to enter the fields of science, technology, engineering and math (STEM) to meet the evolving needs of today’s workforce. The growing emphasis on soft skills across industries and roles, are creating the need for curricula that integrate STEM with the arts.
By integrating the arts into STEM, STEAM-focused curricula incorporate the study of the humanities, language arts, dance, drama, music, visual arts, design, new media and more. Students who explore and master any of these subjects can make themselves more marketable in today’s workforce, as 57 percent of senior leaders value soft skills more than hard skills, In 2019, LinkedIn report notes that creativity, persuasion and collaboration are the top three skills companies seek in prospective employees.
While STEM focuses explicitly on the hard scientific, technological, engineering or mathematical skills to drive progress or create a new concept. In STEAM curricula, students leverage both hard and soft skills to solve problems.
 Urgency of Incorporating Art into STEAM
Urgency of Incorporating Art into STEAM
Art plays a crucial role in the STEAM (Science, Technology, Engineering, Arts, and Mathematics) education framework, bringing creativity, innovation, and a human-centered perspective to the disciplines typically associated with STEM.
Here are some reasons highlighting the urgency of incorporating art into STEAM:
- Fostering Creativity and Innovation:
Art encourages divergent thinking, imagination, and creativity. By integrating art into STEAM, students are empowered to think outside the box, explore unconventional solutions, and approach problems from multiple perspectives. This creativity is vital for innovation and pushing the boundaries of scientific and technological advancements.
- Humanising Technology:
While STEM disciplines often focus on functionality and efficiency, art brings the human element to technology. Art helps in designing user-friendly interfaces, aesthetically appealing products, and interactive experiences that prioritise human needs, emotions, and experiences. This human centered approach enhances the usability and acceptance of technology.
- Enhancing Communication and Expression:
Art provides a unique medium for self-expression and communication. By incorporating art into STEAM, students can effectively communicate their scientific and technological ideas visually, metaphorically, or through interactive installations. This enables them to convey complex concepts and engage diverse audiences beyond traditional scientific communication.
- Cultivating Critical and Aesthetic Thinking:
Art education cultivates critical thinking skills and the ability to analyse, interpret, and evaluate visual information. These skills are valuable in understanding and critically assessing scientific data, visualising scientific concepts, and making informed judgments. The integration of art in STEAM nurtures a holistic approach to problem-solving.
- Promoting Collaboration and Interdisciplinary Thinking:
The inclusion of art in STEAM encourages interdisciplinary collaboration, bringing together artists, scientists, engineers, and technologists. By collaborating on projects, students learn to leverage diverse perspectives, integrate multiple disciplines, and foster a culture of collaboration essential for solving complex real-world challenges.
- Encouraging Adaptability and Resilience:
The arts emphasise experimentation, iteration, and embracing failures as part of the creative process. Integrating art into STEAM instills a growth mindset, encouraging students to embrace challenges, learn from setbacks, and persist in the face of adversity. This resilience is vital in navigating the rapidly evolving technological landscape.
- Addressing Ethical and Social Implications:
Art helps explore the ethical, social, and cultural implications of scientific and technological advancements. It encourages critical examination of the consequences of innovation, raises important questions about ethics, privacy, equity, and inclusivity, and prompts discussions on the responsible development and deployment of technology.
- Career Opportunities in Creative Industries:
The integration of art in STEAM prepares students for a wide range of career opportunities. It equips them with a combination of technical skills, creative thinking, and the ability to bridge disciplines. This positions them well for careers in design, user experience, game development, media arts, creative technology, and other emerging fields.
Incorporating art in STEAM education is urgent to foster creativity, humanise technology, cultivate critical thinking, promote collaboration, address ethical implications, and prepare students for the demands of the modern world. By embracing art as an integral part of STEAM, we wish to nurture well-rounded individuals who are better equipped to tackle complex challenges, drive innovation, and shape a more inclusive and sustainable future.

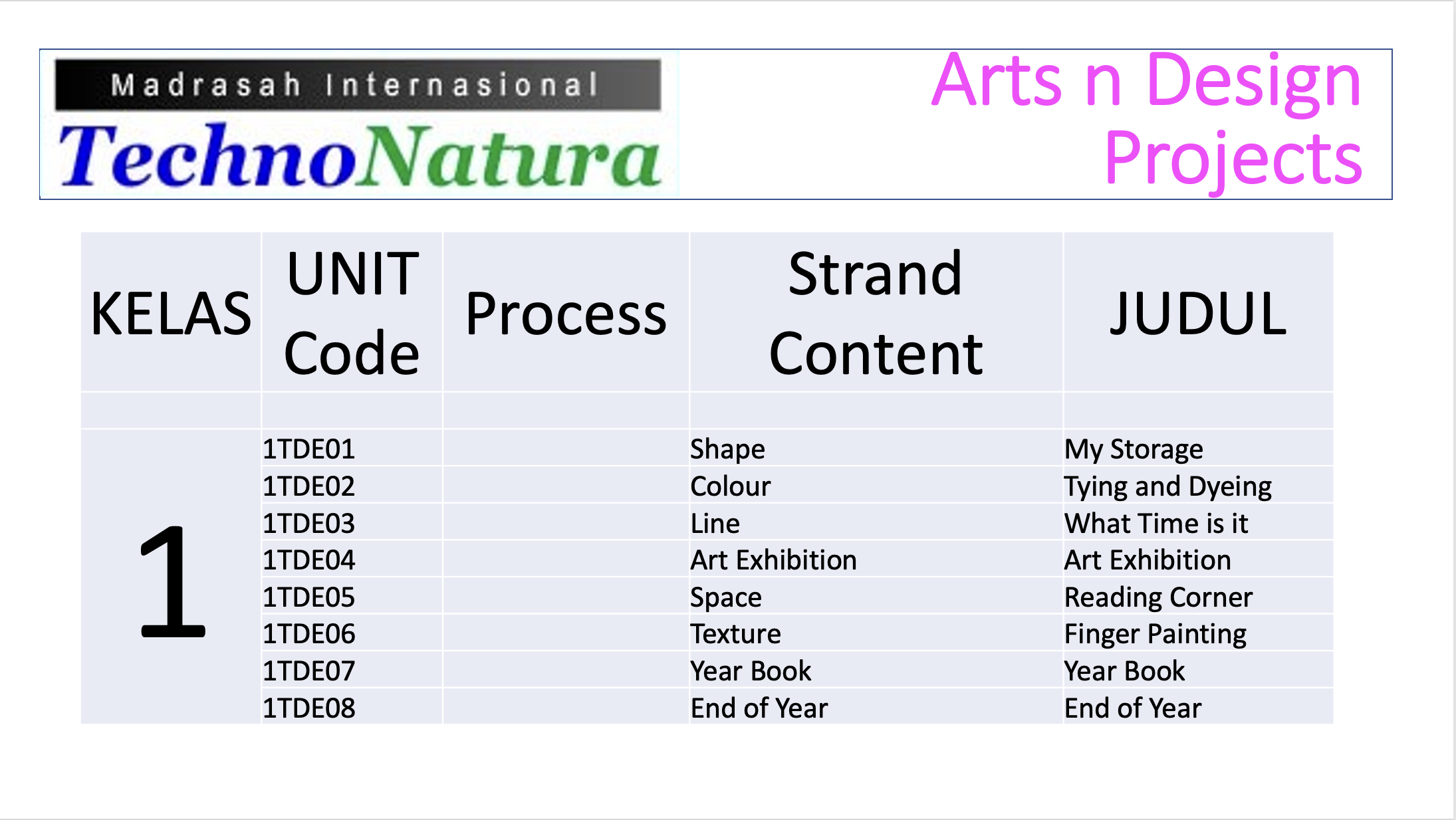
TechnoNatura Approach to STEAM Education ( ART incorporation)
TechnoNatura use Project-based learning (PBL) in a teaching and learning approach that involves students working on an art project over an extended period of time. When applied to art education, project-based learning is a highly effective method for engaging students, fostering creativity, and developing artistic skills

Art Education @ TechnoNatura
Art education is a branch of education that focuses on teaching and learning about the visual arts, including drawing, painting, sculpture, photography, and other creative mediums. It encompasses a wide range of approaches, from hands-on artistic creation to art history, criticism, aesthetics, and the exploration of various artistic styles and movements. Here are some key aspects of art education:
-
Creativity and Self-Expression: Art education fosters creativity and encourages individuals to express themselves through artistic mediums. It provides a platform for personal exploration, allowing students to communicate their thoughts, emotions, and experiences in unique and meaningful ways.
-
Visual Literacy: Art education develops visual literacy skills, enabling individuals to interpret, analyse, and critically engage with visual images and artworks. It teaches students to understand and appreciate the elements of art, principles of design, and the visual language used in different artistic expressions.
-
Cultural and Historical Understanding: Art education exposes students to diverse artistic traditions, cultures, and historical periods. It helps them understand the role of art in reflecting and shaping societies, exploring different artistic movements, and appreciating the cultural and historical significance of artworks.
-
Critical Thinking and Problem-Solving: Art education cultivates critical thinking skills by encouraging students to analyse and interpret artworks, make informed judgments, and develop their own artistic ideas. It fosters problem-solving abilities, as students navigate artistic challenges, experiment with materials, and find innovative solutions to artistic problems.
-
Sensory and Emotional Development: Engaging in art activities stimulates sensory experiences, as students work with different textures, colours, and materials. Art education also promotes emotional development by allowing individuals to express and explore their feelings, helping them develop self-awareness and emotional resilience.
-
Collaboration and Communication: Art education often involves collaborative projects and group critiques, fostering communication and teamwork skills. Students learn to effectively communicate their artistic ideas, give and receive constructive feedback, and work together to create collective artworks.
-
Multidisciplinary Connections: Art education intersects with various other disciplines, including science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM). It promotes interdisciplinary thinking, encouraging students to explore connections between art and other subjects, fostering a holistic understanding of the world.
-
Personal Growth and Well-being: Engaging in art can have therapeutic effects, promoting relaxation, stress reduction, and a sense of well-being. Art education provides an outlet for self-expression and personal growth, nurturing students' confidence, self-esteem, and overall mental and emotional well-being.
-
Career Opportunities in the Arts: Art education lays the foundation for pursuing careers in the arts, such as fine arts, design, illustration, art therapy, art education, museum curation, and art administration. It equips students with the technical skills, creative thinking, and cultural understanding necessary for artistic professions.
Art education benefits individuals of all ages and backgrounds, promoting creativity, critical thinking, cultural understanding, and personal development. It fosters an appreciation for the arts and cultivates skills that are valuable not only in artistic pursuits but also in various other areas of life.
When teaching art, TechnoNatura is trying to provide a well-rounded curriculum that covers various aspects of artistic knowledge and skills. Here are some key areas in our art lessons:
-
Foundations of Art: Teach the fundamental elements of art, including line, shape, form, colour, value, texture, and space. Help students understand how these elements can be used to create visually pleasing and expressive artwork.
-
Principles of Design: Introduce the principles of design, such as balance, proportion, contrast, unity, emphasis, rhythm, and movement. Students learn how these principles contribute to the overall composition and visual impact of their artwork.
-
Drawing Skills: Focus on developing drawing skills, including observation, contour drawing, shading, perspective, and composition. Help students practice and refine their drawing techniques through still life, figure drawing, and landscape studies.
-
Painting Techniques: Introduce various painting techniques, such as color mixing, brushwork, layering, and glazing. Teach students how to work with different paint mediums, such as watercolor, acrylics, or oils, and guide them in creating expressive paintings.
-
3D Art: Explore three-dimensional art forms, including using 3D printing that explore form, texture, and space.
-
Printmaking: Introduce printmaking techniques, such as Batik, ecoprinting. relief printing, monoprinting, or screen printing. Students learn how to create multiple prints, explore texture and pattern, and experiment with various printing methods.
-
Digital Art and Media: Incorporate digital art into the curriculum, introducing students to digital tools and software for creating digital illustrations, graphic design, or multimedia projects. Teach them how to use digital art tools effectively and explore the possibilities of digital creativity.
-
Art History and Context: Introduce students to key artists, art movements, and historical periods, providing a broader understanding of art's cultural and historical significance. Discuss how artistic styles and techniques have evolved over time and encourage students to make connections between historical artworks and their own creations.
-
Art Critique and Analysis: Teach students how to analyse and critique artworks, including their own and those of their peers. Help them develop skills in providing constructive feedback, discussing artistic choices, and understanding the intentions and impact of different artworks.
-
Cultural and Global Perspectives: Explore art from different cultures and regions around the world. Students learn about diverse artistic traditions, indigenous art, and the cultural significance of artworks, fostering appreciation for cultural diversity and promoting global awareness.
-
Contemporary and Experimental Art: Introduce students to contemporary art practices, experimental approaches, and innovative techniques. Students are encouraged to explore unconventional materials, conceptual art, installations, performance art, or new media to broaden their artistic horizons.
-
Artistic Expression and Personal Voice: Encourage students to develop their unique artistic style and voice. Provide opportunities for personal expression, self-reflection, and exploration of individual themes and concepts in their artwork.
TechnoNatura strive to create a balance between structured lessons and opportunities for creative exploration. Tailor our teaching to the age, skill level, and interests of our students, and encourage students to take ownership of their artistic learning. Art education is aiming ot foster creativity, critical thinking, cultural understanding, and personal growth.
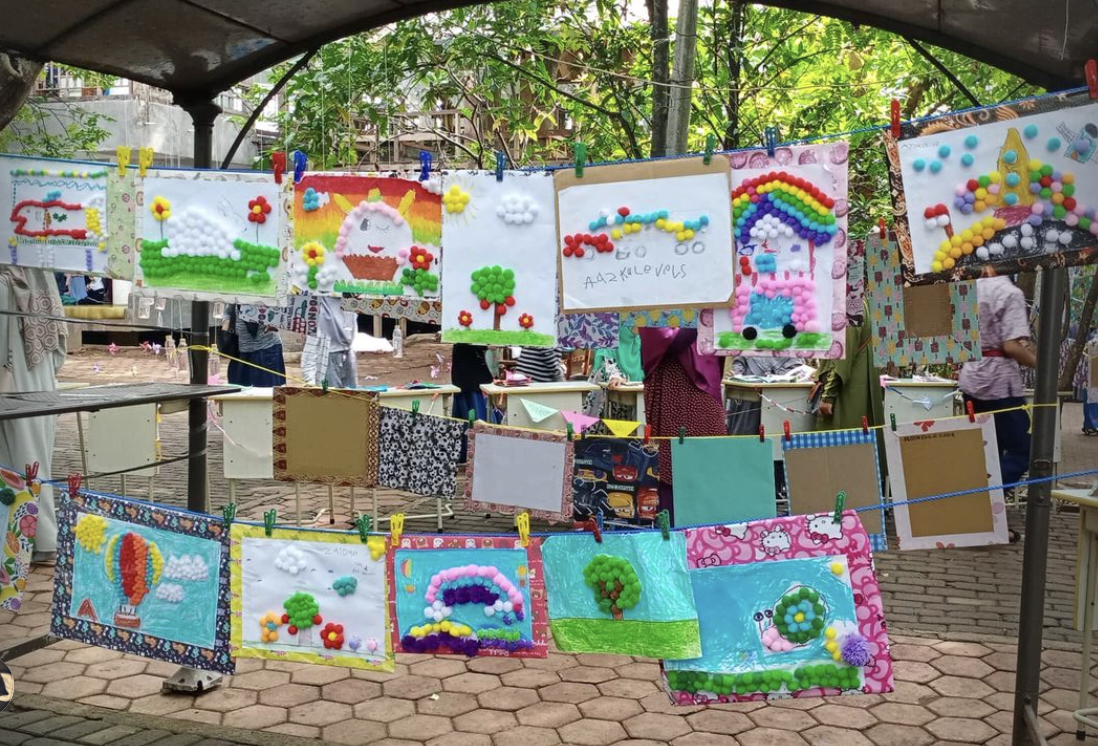





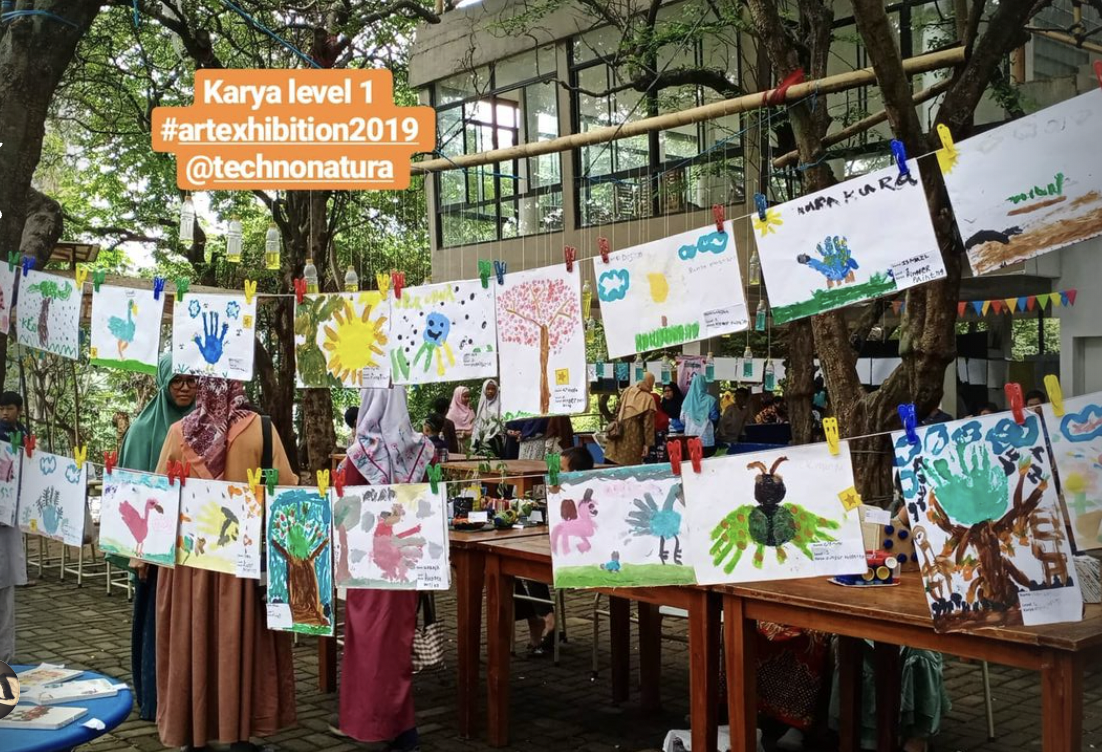
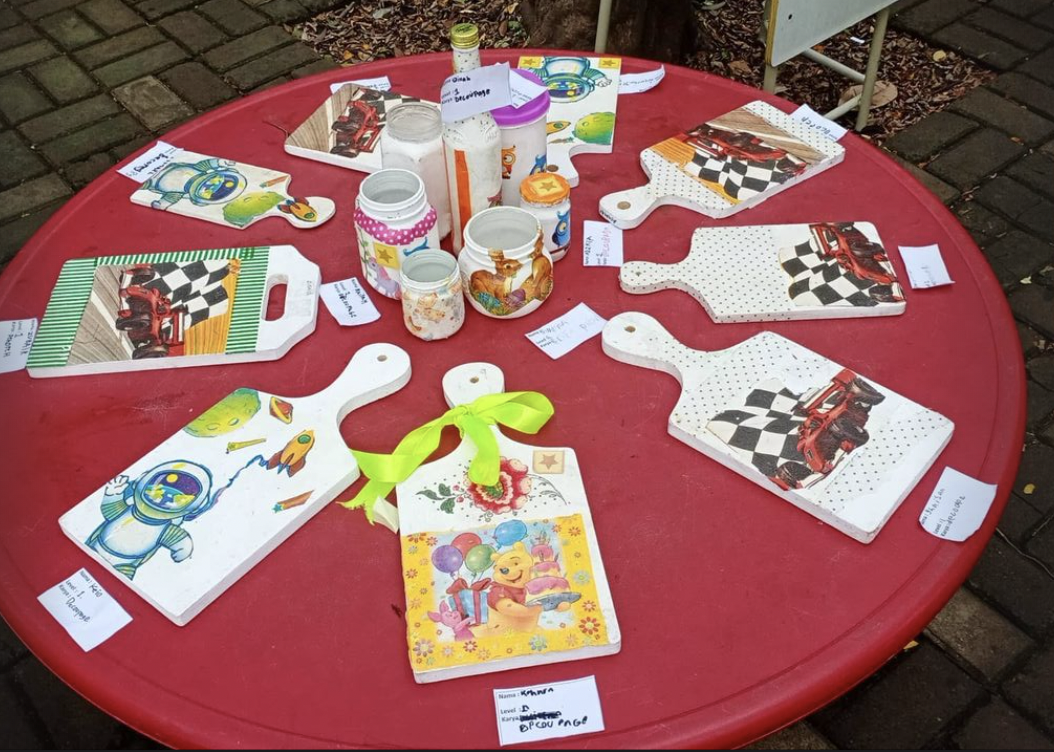
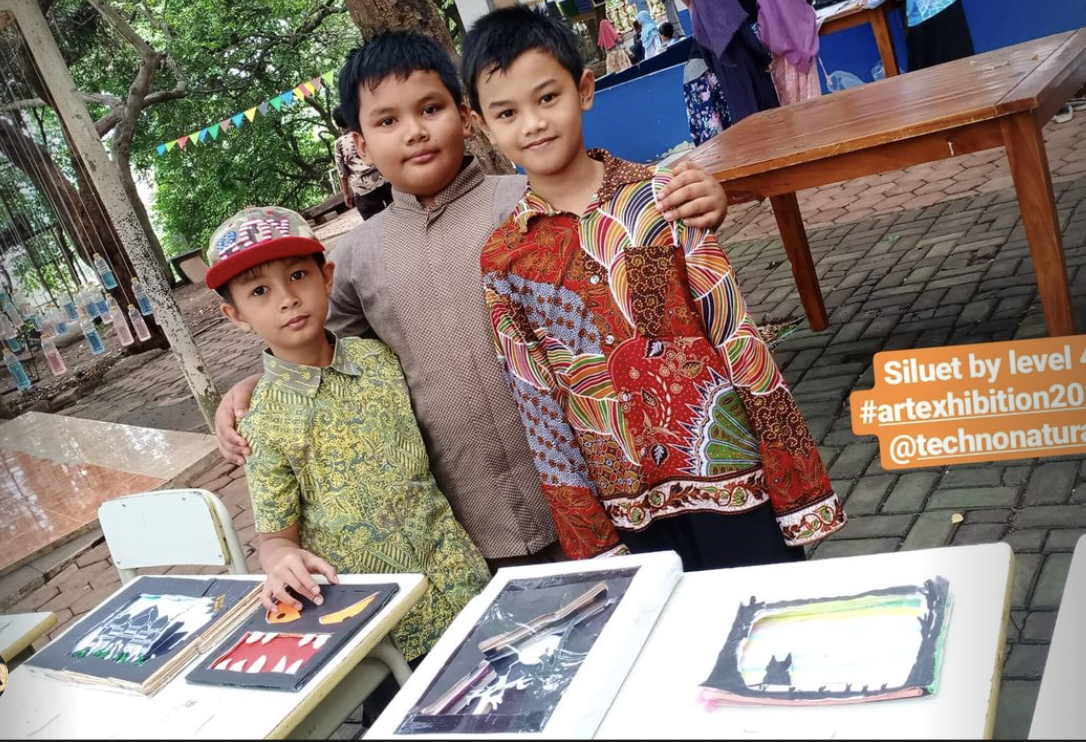
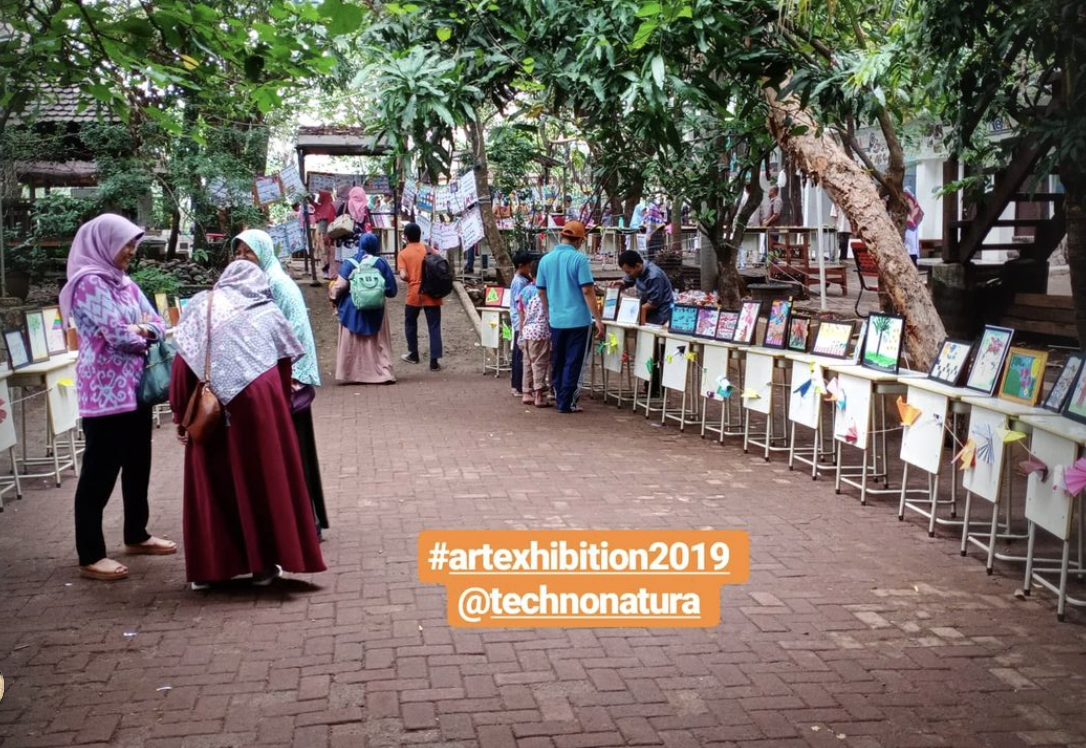
TechnoNatura Student Art Exhibition
An annual student art exhibition is a showcase of artworks created by TechnoNatura students. It provides an opportunity for students to share their artistic talent, creativity, and growth with a wider audience. Here's an overview of a TechnoNatura student art exhibition:
-
Organising Committee: A team of students, teachers, and possibly art professionals or mentors collaborate to organise the exhibition. They handle logistics, curatorial decisions, promotion, and coordination of the event.
-
Venue Selection: Choose a suitable venue within the school or a local gallery or community space that can accommodate the artworks and provide an engaging setting for viewers.
-
Theme or Focus: Decide on a theme or focus for the exhibition, if desired. It could be based on a particular artistic style, concept, or subject matter to create a cohesive display of the student artworks.

-
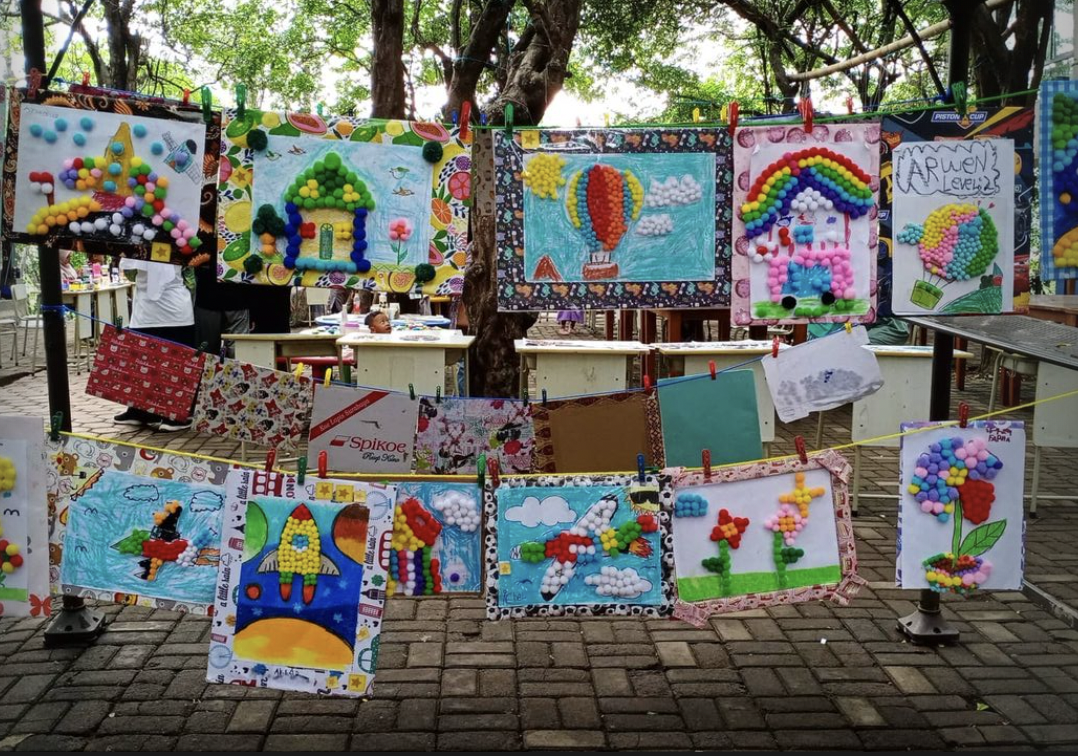
Artwork Selection: Establish criteria for artwork submissions and select the pieces that will be included in the exhibition. Consider diversity in mediums, styles, and skill levels to showcase a broad range of student artistic expression.

-
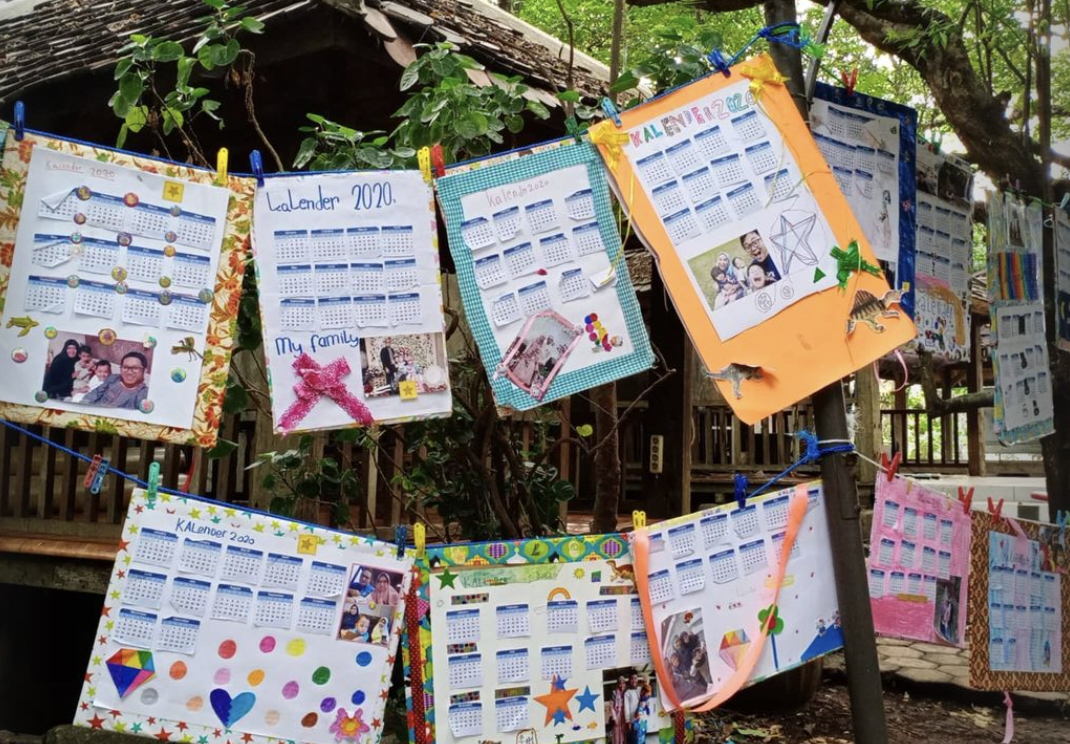
Artwork Preparation: Help students prepare their artworks for display. This may involve framing or mounting artwork, ensuring proper labelling, and ensuring that all pieces are ready for exhibition.

-
Curatorial Process: Determine the arrangement and placement of the artworks within the exhibition space. Consider the flow, visual impact, and any narrative or conceptual connections between the pieces.
-
Opening Reception: Plan an opening reception for the exhibition, inviting students, their families, teachers, school staff, and the broader community. The reception can include speeches, performances, refreshments, and opportunities for attendees to engage with the student artists.
-
Promotion and Publicity: Develop a marketing plan to promote the exhibition within the school and the community. Utilise social media, school newsletters, posters, and local media outlets to generate interest and attract visitors.
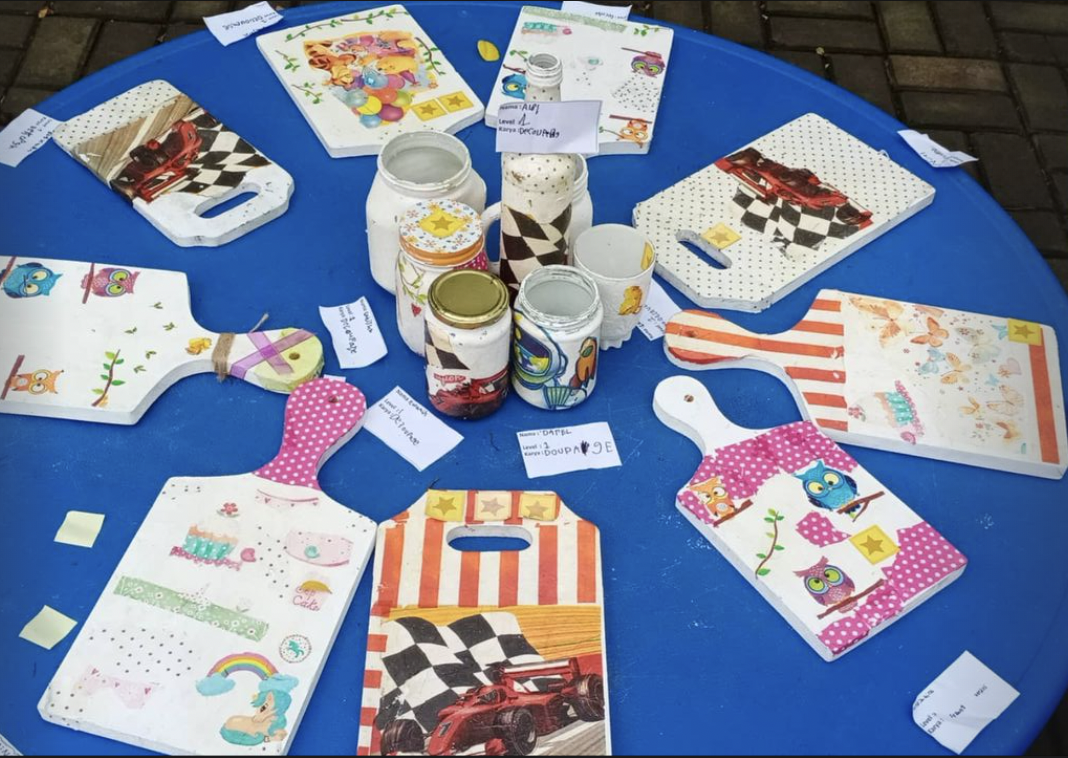

-
Educational Activities: Organise educational activities alongside the exhibition, such as artist talks, workshops, or interactive stations. These activities can enhance the visitors' experience and provide opportunities for students to share their artistic process and techniques.

-
Documentation and Reflection: Capture photographs or videos of the exhibition to preserve the experience and create a record of the students' achievements. Encourage students to reflect on their artistic growth and learning throughout the exhibition process.
-
Duration and Closure: Determine the duration of the exhibition, which can vary based on the availability of the venue and the goals of the event. Once the exhibition concludes, coordinate the removal of artworks and ensure that the exhibition space is returned to its original condition.
A student art exhibition celebrates the creativity and artistic accomplishments of students. It offers them a chance to gain exposure, receive feedback, and develop confidence in their artistic abilities. The exhibition fosters a sense of pride within the school community and encourages the appreciation of art among students, teachers, families, and the wider public.


TechnoNatura International Event
FGC 2018 Mexico city

FGC 2019 Dubai UAE

FGC 2022 Geneva Switzerland
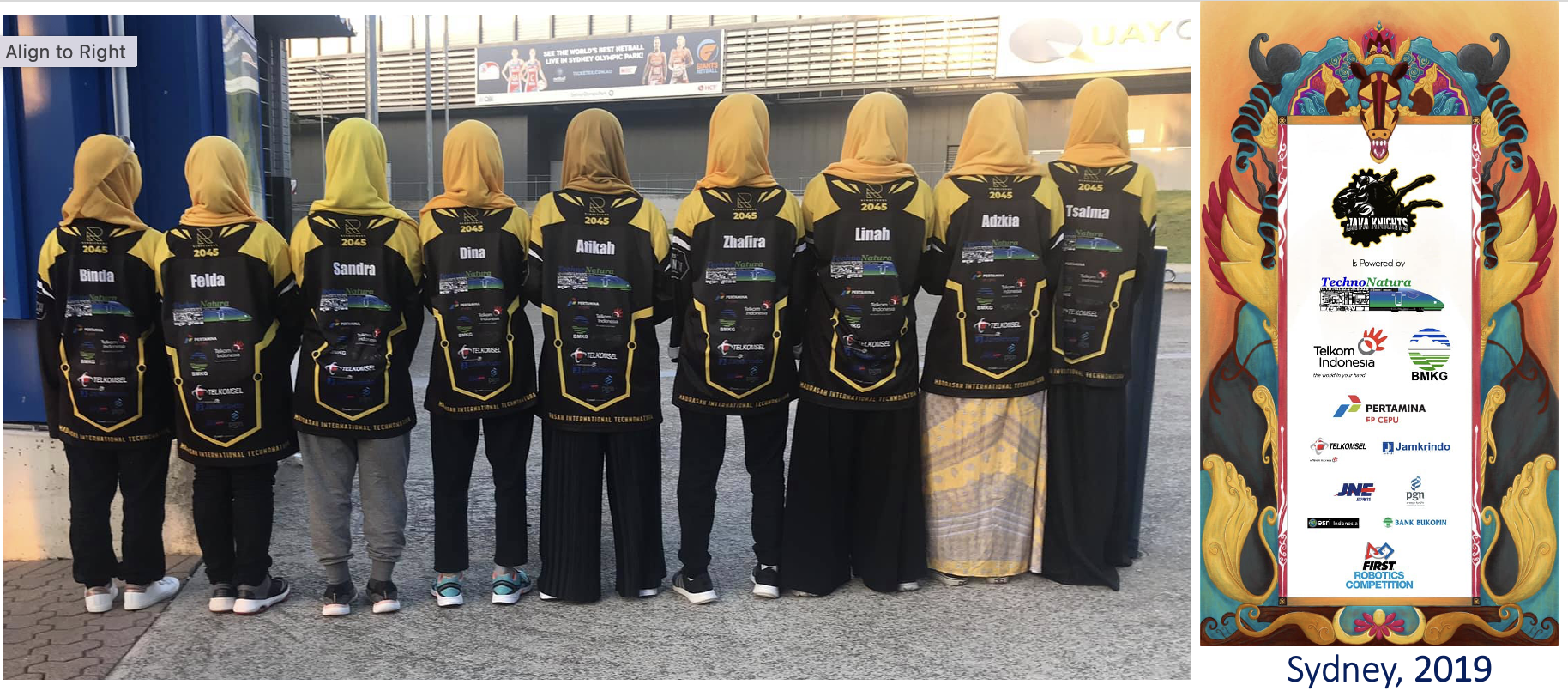
FRC2019 Sydney, and Detroit

FRC2020 Online


TechnoNatura International Arts Awards
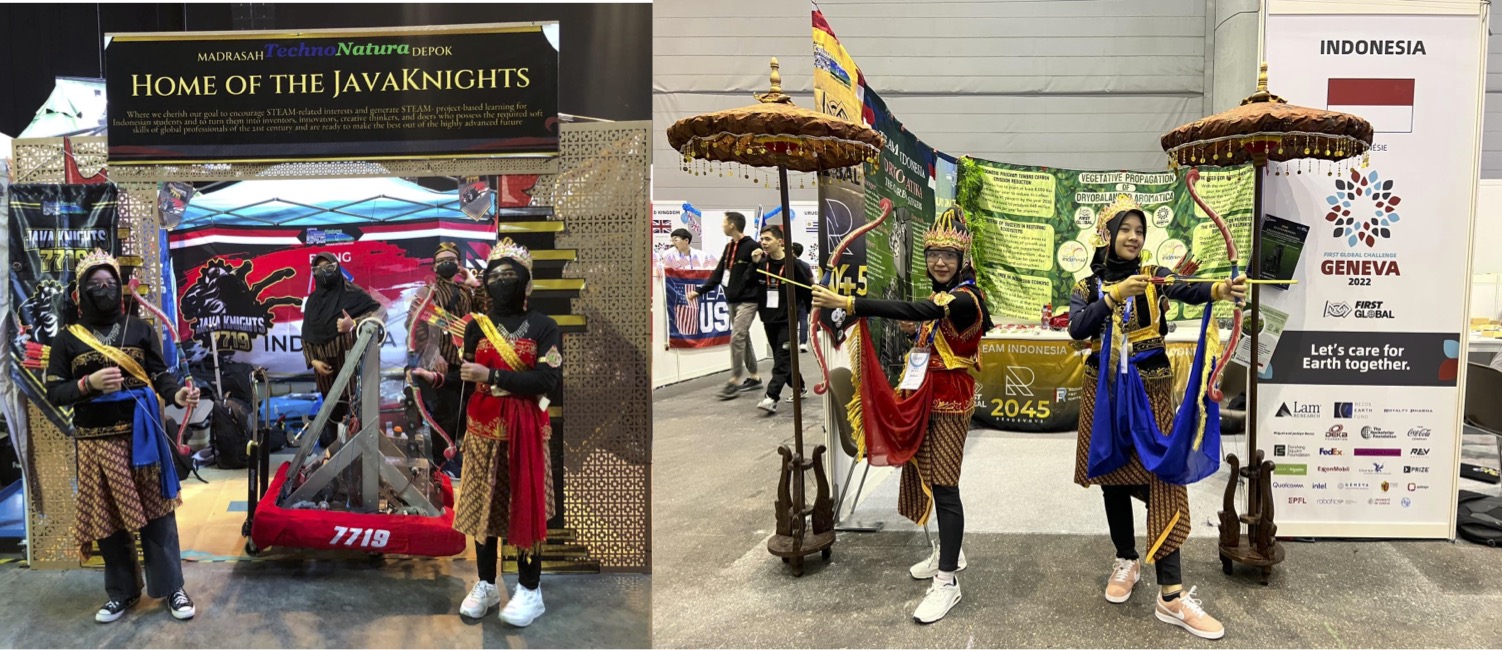
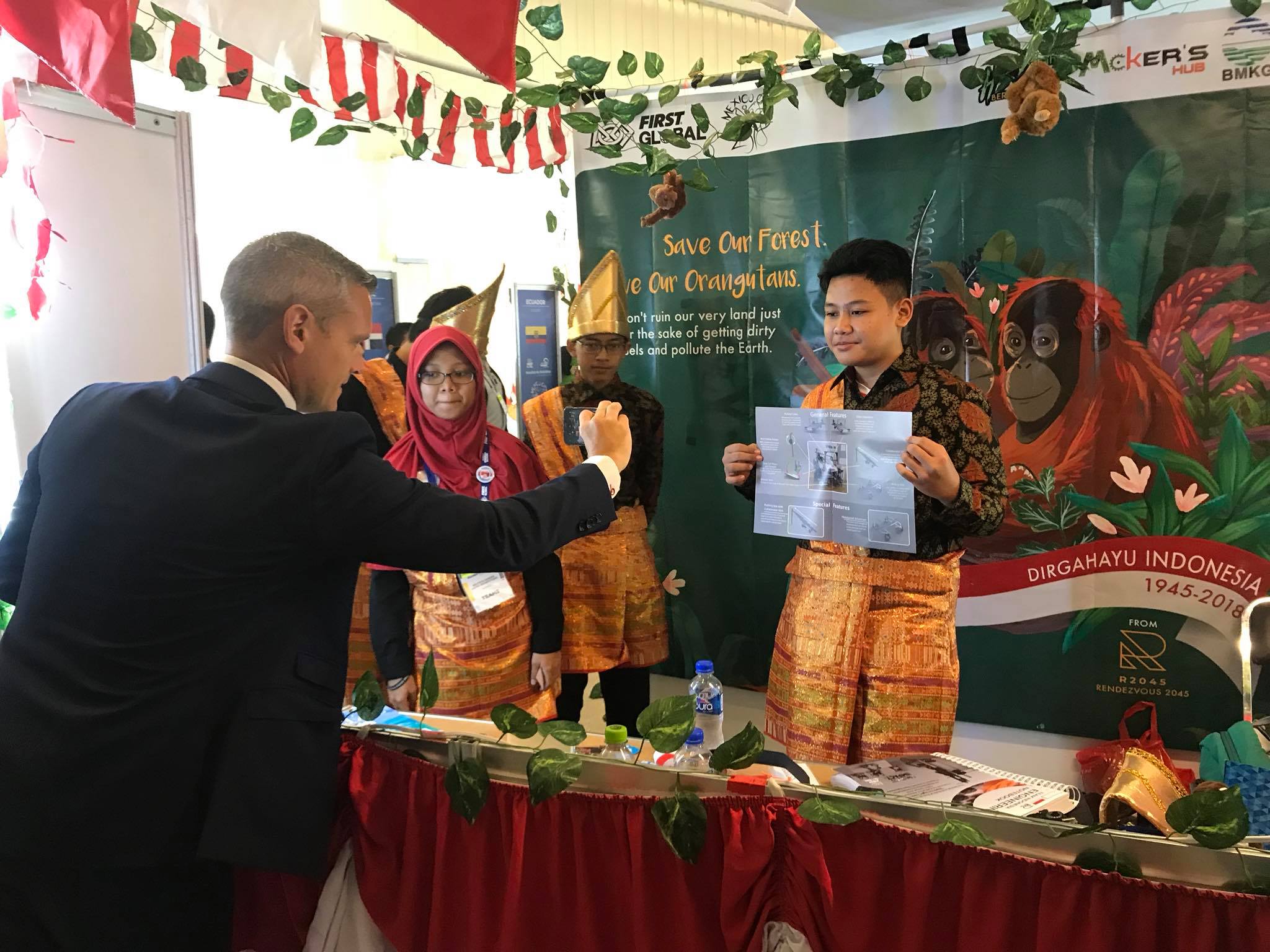
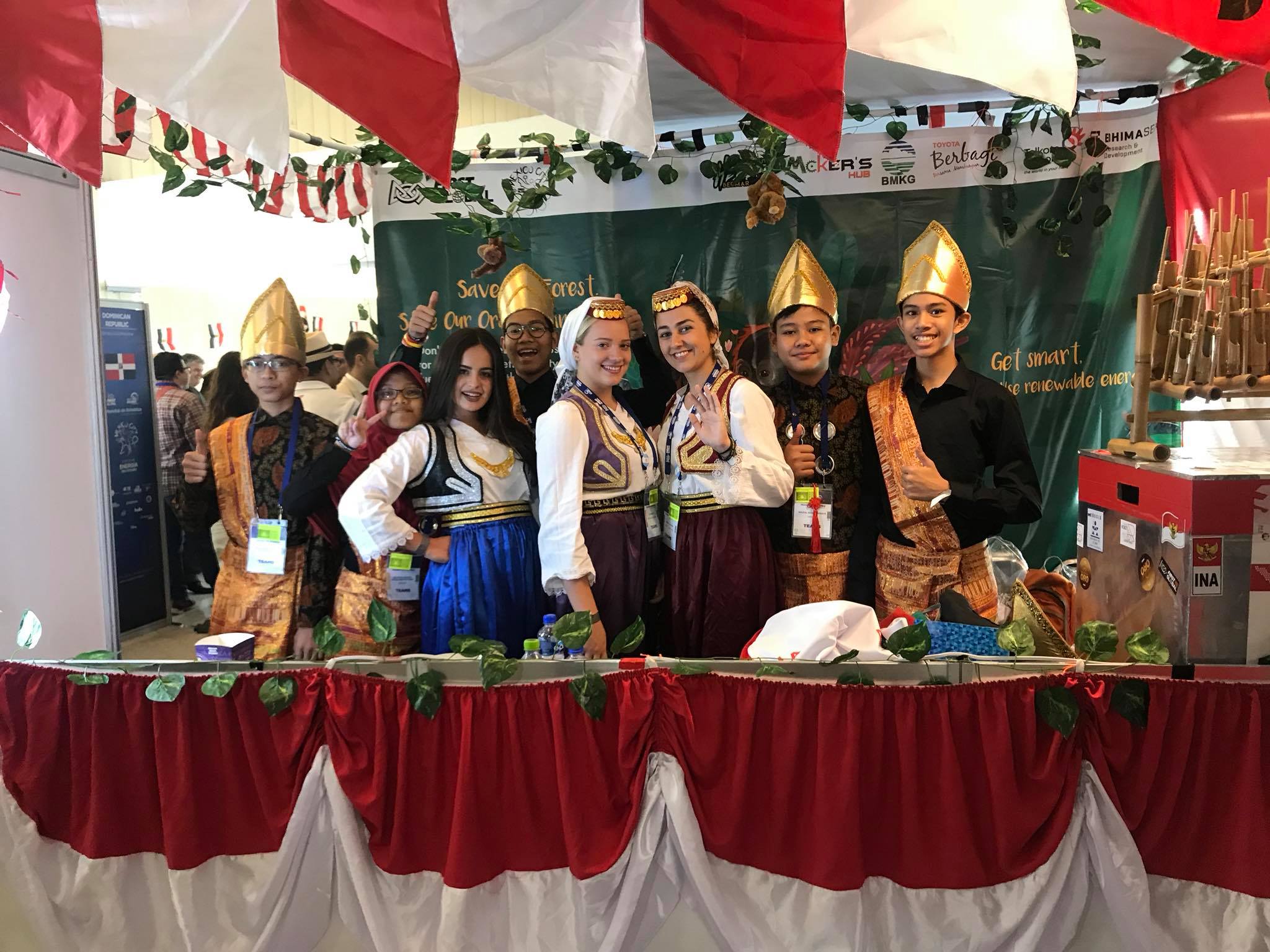
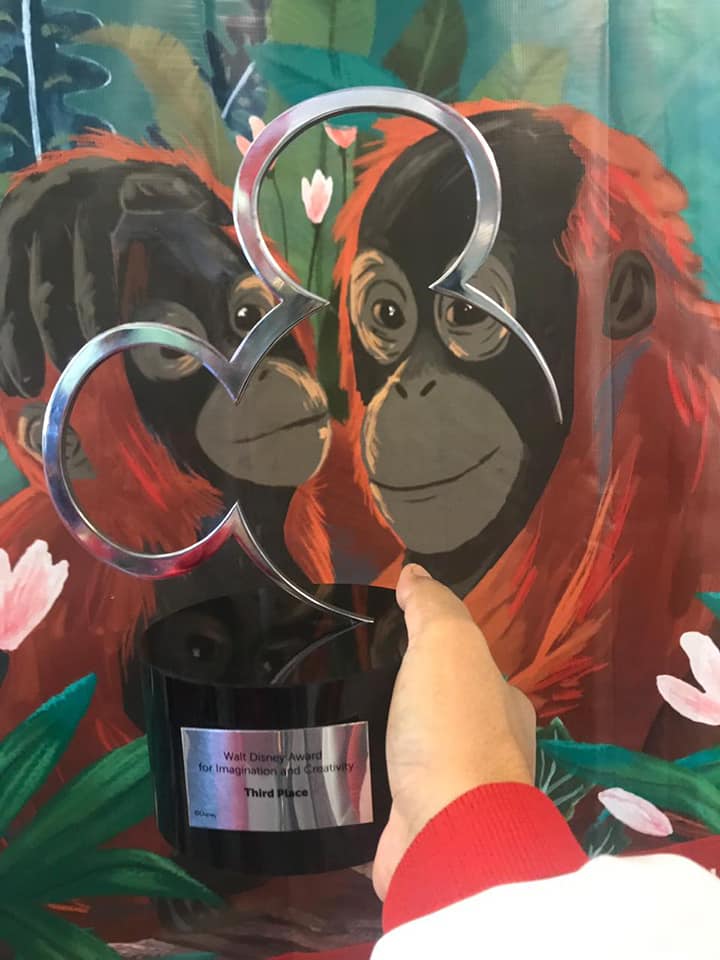
1 Walt Disney Imagination and Creativity Awards, FIRST Global Challenge, Mexico, 2018
In this event Indonesian, Team carried the theme "More than Robots", besides the competing robots, the Indonesian Team carried the message of saving Orangutans and the necessity to build a future for the global young generation to be active in the STEAM field and yet be friendly to the environment.


2. FRC Imagery Award 2022 Istanbul regional
Imagery Award in honour of Jack Kamen. FRC 2022 Istanbul regional
The Imagery Award is an award presented at the FIRST Robotics Competition (FRC), an international high school robotics competition. The FRC is organised by FIRST (For Inspiration and Recognition of Science and Technology), a nonprofit organisation that aims to inspire young people to be science and technology leaders.
The Imagery Award is given to the team that displays outstanding visual aesthetic integration of the machine's appearance, performance, and overall brand image. The award recognises the team's ability to effectively communicate their team identity, enthusiasm, and spirit through the visual presentation of their robot and team attire. The team's use of colours, graphics, and other visual elements to create a cohesive and appealing image is considered in the evaluation process.
The Imagery Award highlights the importance of creativity, visual design, and branding in addition to technical excellence in the FRC. It encourages teams to think beyond just building a functional robot and to also consider the overall visual impact and representation of their team.


- Log in to post comments
